Artificial intelligence (AI) is a popular topic today, and with the rise of AI comes a new vocabulary. As a beginner to this technology, you may come across these terms as you research or harness different AI tools. We’ve compiled a list of the top terms you should know so you can use AI more knowledgeably and effectively.
Large language model (LLM)
A large language model is a type of artificial intelligence that can generate and analyze text or code. You give the model a prompt or question, and it responds with a human-sounding answer. Often, when people refer to AI, they are actually speaking specifically about large language models.

Generative AI
This type of artificial intelligence is trained on a large dataset to identify patterns and create new variations based on those patterns. Generative AI tools create new content ranging from text and images to audio and video. An LLM is just one example of generative AI and uses text.
Machine learning (ML)
This subfield of artificial intelligence deals with a machine’s ability to imitate human behavior. When creating computer models, the goal is to give these models the ability to act intelligently as a human would. Machine learning may involve training machines to understand natural text or recognize visual scenes.
Deep learning
This subset of machine learning aims to simulate how the human brain operates and makes decisions. Deep learning involves passing information through hundreds or thousands of layers of processing. This capability enables computers to take raw, unstructured data and create accurate outputs.
Natural language processing (NLP)
This term represents the ability of digital devices to understand and generate text and speech. Devices gain this capability through a combination of statistical modeling, machine learning, deep learning, and modeling of human language.
Tokens and tokenization
Tokens are small units of text data broken down so an LLM understands them. A token may include characters, words, or phrases. Each LLM developer has a unique system, but typically, 1 token represents several characters. Normally, developers price their products based on tokens.
Tokenization is the process NLP systems use to break text down into smaller units. Once the system divides the text, it can analyze it more effectively to present a human-sounding response.
Application programming interface (API) key
An API key is like a password that lets you access a service. This code identifies and authenticates an application or user.
Within AI models, API keys identify people and grant them access to make requests to the AI system without directly accessing it. For example, you could use an API key to integrate a particular AI model into your application or on your website.
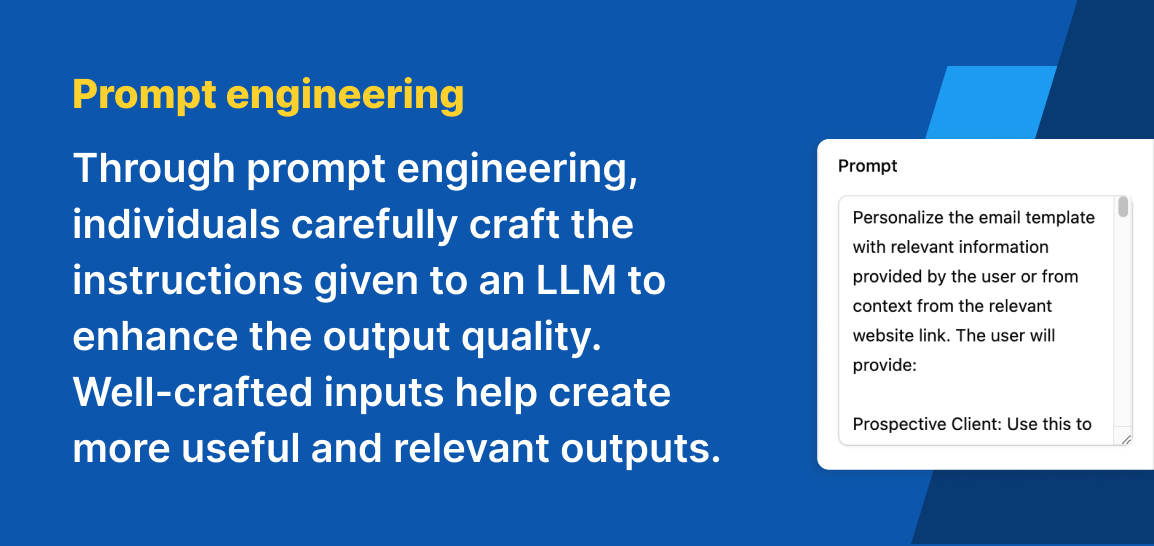
Prompt engineering
While LLMs are meant to supply relevant and human-sounding answers, the quality of their responses vary depending on the quality of the input or prompt.
Through prompt engineering, individuals carefully craft the instructions given to an LLM to enhance the output quality. Well-crafted inputs help create more useful and relevant outputs.
Learn More About Prompt Engineering
Context window
A context window is like an LLM’s working memory or the amount of information it can consider at one time. Larger context windows enable the LLM to process longer inputs and to take into account information from earlier in the exchange.
Longer context windows often mean better accuracy, fewer hallucinations, and more coherent responses.
Latency
In LLMs, latency is the time it takes for an LLM to process a prompt and generate a response. A high latency means the model has to take more time to process the input before it provides an output.
Some models with advanced reasoning capabilities tend to have higher latency due to the added effort it takes to analyze complex science, math, or coding problems. Ideally, latency should be as low as possible so systems can deliver real-time responses.
Grounding
Grounding connects an AI model’s output to verifiable sources of information to reduce the chances of hallucination. Most often, grounding refers to linking the response to internet searches.
With grounding, an LLM can cite its sources so you know where the information came from. It also retrieves the most up-to-date information, which is often not available with AI models since they train on an earlier dataset.
Agent
In the world of AI, agents are like tailored personal assistants built to have particular expertise and help you accomplish tasks more effectively. An AI agent has a specific job and possesses the tools necessary to achieve it.
For example, you could create an agent with knowledge of your particular business and its operations so it can automatically answer customer questions or help you develop content for your website.

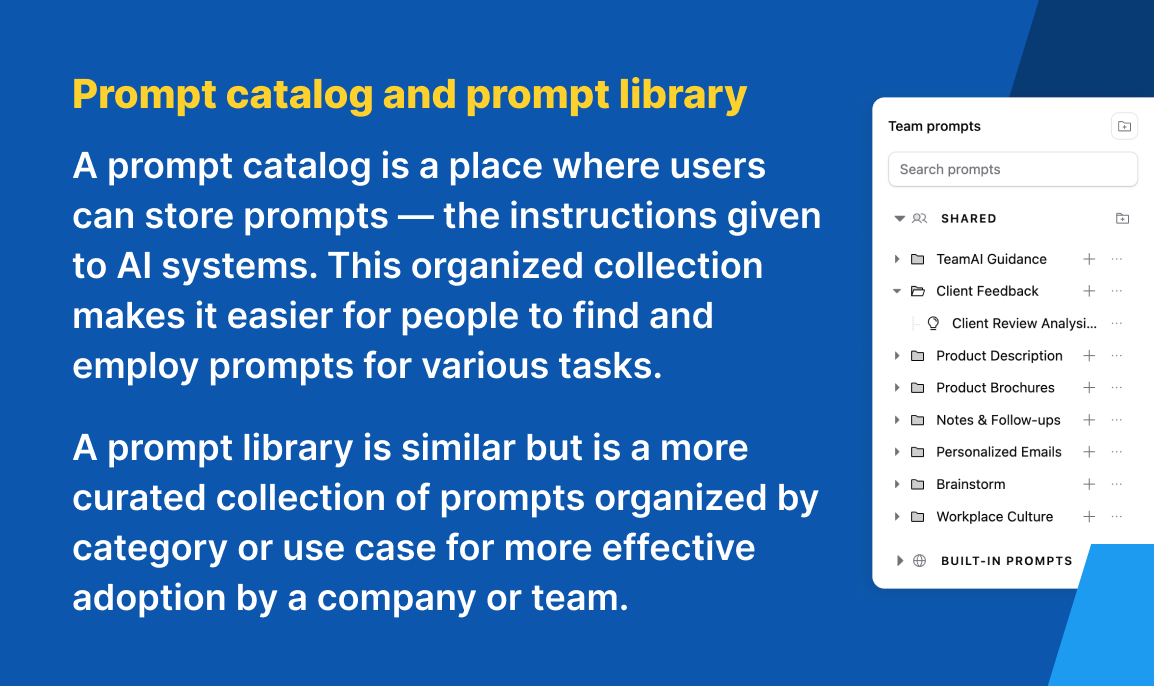
Prompt catalog and prompt library
A prompt catalog is a place where users can store prompts — the instructions given to AI systems. This organized collection makes it easier for people to find and employ prompts for various tasks.
A prompt library is similar but is a more curated collection of prompts organized by category or use case for more effective adoption by a company or team.
Discover TeamAI’s Custom Prompt Libraries
Hallucinations
In the world of AI, hallucinations are results generated by an LLM that are incorrect, misleading, or nonsensical. These outputs typically result from issues with the AI system, like training data biases.
Zero-shot prompting
Zero-shot prompting involves using an LLM’s generalization skills to attempt a new task without any training or examples. This technique varies in effectiveness depending on the quality of the prompt and the complexity of the task.
In contrast, one-shot or few-shot prompting involves giving the model one or a few examples to help guide the output.
Parameters
Parameters refer to the variables an AI model learns during training. The model will employ these internal variables to control predictions or decisions, determining the output for a given input. Usually, more parameters mean the ability to learn more complex patterns within data.
Parameters are closely related to tokens. Tokens are the input an AI model processes, and parameters are the internal settings that determine how a model interprets inputs to understand and generate a response.
Join TeamAI for expertise and innovation
TeamAI is a platform that gives you access to the top LLMs, plus collaboration tools to enhance your work. A dedicated team of developers who are experts in the industry maintain and constantly update the platform with new features and the latest models.
Join TeamAI to use multiple LLMs and other incredible features.
